
Nikon CFI Plan Fluor Objectives feature high transmission from the ultraviolet to the infrared, along with exceptional flatness across the entire field of view. These objectives are ideal multipurpose objectives for a variety of microscopy techniques, including brightfield, fluorescence, polarizing, or DIC microscopy. These microscope objectives are suitable for high contrast fluorescence observation or for applications including photomicrography. Nikon CFI Plan Fluor Objectives have M25 x 0.75 mounting threads. The objectives are available in magnifications from 4X up to 60X.
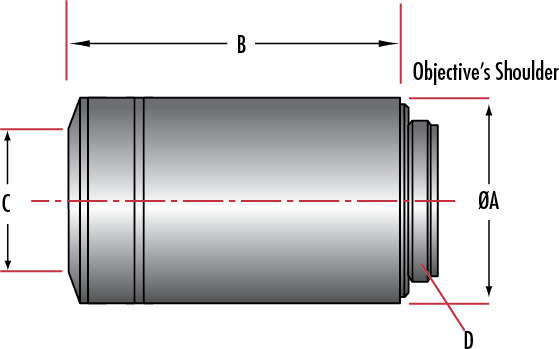
| Dimensions (mm) | ||||||||
| Stock No. | Nikon Model Number | Immersion Liquid | Magnification | Parafocal Length |
A | B | C | D |
| #88-378 | MRH00041 |
N/A |
4X | 60.06 | 30.0 | 42.7 | 16.5 | M25 x 0.75 |
| #88-379 | MRH00101 | N/A | 10X | 60.06 | 30.0 | 42.4 | 18.0 | M25 x 0.75 |
| #38-004 | MRP07220 | Water | 16X | 75.0 | 35.0 | 72.0 | 6.0 | M32 x 0.75 |
| #88-380 | MRH00201 | N/A | 20X | 60.06 | 28.0 | 57.8 | 8.5 | M25 x 0.75 |
| #88-381 | MRH00405 | N/A | 40X | 60.06 | 30.0 | 59.2 | 10.0 | M25 x 0.75 |
| #88-382 | MRH00602 | N/A | 60X | 60.06 | 31.5 | 59.2 | 5.0 | M25 x 0.75 |
or view regional numbers
QUOTE TOOL
enter stock numbers to begin
Copyright 2023, Edmund Optics India Private Limited, #267, Greystone Building, Second Floor, 6th Cross Rd, Binnamangala, Stage 1, Indiranagar, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India 560038
California Consumer Privacy Acts (CCPA): Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information
California Transparency in Supply Chains Act
The FUTURE Depends On Optics®